How many bitcoins will ever be created
If you’re interested in Bitcoin, you may have wondered how many of them will ever exist. Unlike traditional currencies that are issued by central banks, Bitcoin has a fixed supply limit of 21 million units. This limit is hardcoded into the Bitcoin protocol, which means it cannot be changed without consensus from the Bitcoin community.
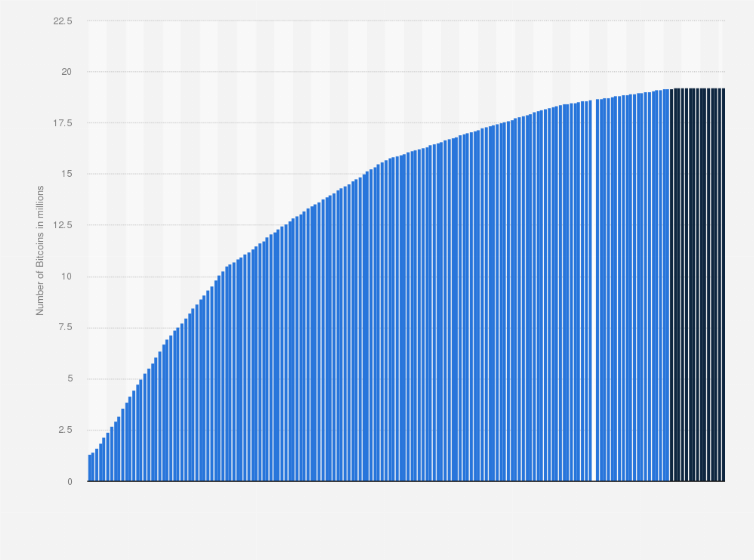
As of now, over 18 million bitcoins have been mined, leaving around 3 million left to be generated. However, the rate at which new bitcoins are created decreases every four years due to a process called halving. This means that the remaining 3 million bitcoins will take longer to produce than those already mined.
The first halving occurred in 2012 when the mining reward was cut from 50 BTC per block to 25 BTC. The second halving took place in 2016, where the reward dropped to 12.5 BTC per block. And the third halving occurred in May 2020, reducing the reward to 6.25 BTC per block.
Based on this halving process, it is estimated that the last Bitcoin will be mined in the year 2140. At that point, the total number of bitcoins in circulation will be 21 million, and no more bitcoins will ever be produced.
It’s worth noting that not all of the existing bitcoins are accessible or even available for use. Some early adopters have lost access to their bitcoin wallets, while others have chosen to hold onto their coins as a long-term investment.
In conclusion, the maximum number of bitcoins that will ever exist is 21 million, with over 18 million already in circulation. The remaining 3 million will be generated gradually through the mining process, with the final bitcoin expected to be mined in the year 2140.
The Role of Mining in Bitcoin Creation
Bitcoin is a digital currency that has become more popular in recent years, and its creation process has become a hot topic of discussion. The role of mining in Bitcoin creation is an essential part of understanding how this cryptocurrency is created.
Mining is the process by which new Bitcoins are created and added to the blockchain network. It is achieved by solving complex mathematical problems using specialized computer hardware called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). Miners validate transactions on the network and add them to the blockchain, which results in the creation of new Bitcoins as a reward.
The mining process plays a crucial role in Bitcoin creation, as it ensures that the network remains secure and reliable. The decentralized nature of Bitcoin means that there is no central authority or entity controlling the network. Instead, miners provide the computational power necessary to maintain and secure the network.
In addition to creating new Bitcoins, the mining process also serves to verify and validate all Bitcoin transactions. Every transaction is verified by multiple nodes on the network before being added to the blockchain. This process ensures that every Bitcoin transaction can be trusted and prevents the possibility of fraudulent activity.
However, the mining process is not without its controversies. The high energy consumption required for mining has led to concerns about its environmental impact. Some critics argue that Bitcoin mining contributes to climate change and encourages the use of fossil fuels.
Despite these concerns, the role of mining in Bitcoin creation remains vital. Without miners, the network could not function, and Bitcoin would not exist. As the demand for Bitcoin continues to grow, so too will the importance of mining in its creation process.
In conclusion, mining plays a crucial role in the creation of Bitcoin, ensuring the security and reliability of the network. While there are concerns about its environmental impact, the mining process remains an essential part of Bitcoin’s future. As the world becomes increasingly digital, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are likely to become even more important, making the role of mining even more critical.
The Future of Bitcoin Production
Bitcoin, the world’s first decentralized digital currency, has revolutionized the way people think about money. Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has gained widespread popularity, and as of today, it is one of the most widely traded cryptocurrencies globally. However, there is more to Bitcoin than just trading; the process of creating new Bitcoins, known as Bitcoin production, is equally fascinating.
Bitcoin production, also known as Bitcoin mining, is the process of adding new Bitcoin transactions to the blockchain ledger. Miners compete to validate these transactions by solving complex mathematical equations. The first miner to solve the equation receives a reward in the form of newly minted Bitcoins. This process ensures that Bitcoin transactions are secure, transparent, and virtually tamper-proof.
The future of Bitcoin production looks bright, with a steady increase in demand for cryptocurrencies worldwide. The number of active Bitcoin miners has grown substantially over the years, and this trend is expected to continue in the coming years. As the number of miners increases, so does the computing power of the network, making it even more secure.
One of the major challenges facing Bitcoin production is energy consumption. Bitcoin mining requires a significant amount of computing power, which translates into high energy consumption. To counter this, miners are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Another exciting development in the world of Bitcoin production is the rise of cloud mining. Cloud mining allows users to mine Bitcoin without having to invest in expensive hardware or software. Instead, users can rent computing power from cloud mining providers and earn rewards based on the amount of power they contribute.
In conclusion, the future of Bitcoin production looks promising, with increasing demand and innovation driving the industry forward. While there are challenges to overcome, such as energy consumption and scalability, the benefits offered by Bitcoin mining make it an essential part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As we move towards a more decentralized future, Bitcoin production will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of money.
Exploring the Bitcoin Block Reward
Are you curious about Bitcoin’s block reward? If so, you’re in the right place. In this article, we will explore what the Bitcoin block reward is and how it affects the cryptocurrency market.
When Bitcoin was first created in 2009, it was designed to be a deflationary currency. This means that there would only ever be 21 million Bitcoins in existence. To ensure that new Bitcoins could still be introduced into the market, the creators of Bitcoin implemented what is known as the block reward.
The block reward is essentially a prize given to miners for solving complex mathematical problems and adding a new block to the blockchain. When Bitcoin was first created, the block reward was set at 50 Bitcoins per block. However, every 210,000 blocks, or roughly every four years, the block reward is cut in half. This is known as the halving.
The most recent halving occurred in May 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 Bitcoins to 6.25 Bitcoins. The next halving is set to occur in 2024 when the block reward will be reduced to 3.125 Bitcoins.
So why does the block reward matter? Well, it directly impacts the supply of Bitcoin in the market. As the block reward decreases, the rate at which new Bitcoins are introduced into the market also decreases. This creates a scarcity effect, which can drive up the price of Bitcoin.
Additionally, the block reward serves as an incentive for miners to continue verifying transactions on the network. Without the block reward, it’s possible that miners may not have enough of a financial incentive to continue securing the network.
In conclusion, the block reward is an essential part of the Bitcoin ecosystem. It ensures that new Bitcoins can be introduced into the market while also incentivizing miners to continue verifying transactions. The halving events that occur every four years create a scarcity effect that can impact the price of Bitcoin. So next time you hear about the block reward, you’ll know exactly what it means and why it matters.
How Bitcoin’s Supply Affects Its Value
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that has been gaining momentum in recent years. One of the most unique features of Bitcoin is its limited supply of 21 million coins, which sets it apart from traditional currencies. In this article, we will explore how Bitcoin’s supply affects its value.
The limited supply of Bitcoin is a key factor in determining its value. Unlike fiat currencies such as the US dollar or Euro, which can be printed at will by central banks, the supply of Bitcoin is fixed. This means that as demand for Bitcoin increases, its price also increases due to its scarcity.
Another aspect that affects Bitcoin’s value is the rate at which new Bitcoins are added to the market. Bitcoin mining, the process by which new Bitcoins are created and added to the circulating supply, is designed to become increasingly difficult over time. As more miners join the network, the difficulty level of mining Bitcoin increases, resulting in a slower rate of new coin creation.
This slow and steady rate of new coin creation is intended to maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin and prevent inflation. As the number of new Bitcoins being mined decreases, the supply becomes even more limited, driving up the value of existing coins.
However, it’s worth noting that factors beyond the limited supply of Bitcoin can also affect its value, including market sentiment, government regulations, and adoption rates. Volatility is also a significant characteristic of Bitcoin’s value, with sharp fluctuations occurring regularly.
In conclusion, Bitcoin’s limited supply plays a crucial role in determining its value. As demand for Bitcoin grows, the limited supply and slow rate of new coin creation contribute to its scarcity, driving up its price. However, other factors can also impact its value, making it essential to stay informed on developments in the cryptocurrency market.
The Distribution of Bitcoin Ownership
Bitcoin has become a household name in recent years, but have you ever wondered who actually owns it? Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries such as banks. This means that anyone with an internet connection can own and trade bitcoin, and there’s no central authority controlling its distribution.
Despite being a decentralized currency, the distribution of bitcoin ownership is not evenly spread out. In fact, a small number of individuals and entities hold a significant amount of the total bitcoin supply. According to data from Chainalysis, around 2% of addresses control 95% of the bitcoins in circulation.
These addresses are often referred to as “whales” in the cryptocurrency community, and they’re able to influence the market by buying or selling large amounts of bitcoin at any given time. This concentration of ownership can be seen as a potential risk to the stability of the bitcoin market, as the actions of a small number of whales could significantly impact the price of bitcoin.
However, it’s important to note that the distribution of bitcoin ownership is constantly changing. As more people adopt bitcoin and buy it for themselves, the concentration of ownership may become less severe. Additionally, some of the largest bitcoin holdings belong to exchanges and custodians, which hold bitcoin on behalf of their users. This means that while the addresses may appear to be controlled by a single entity, the actual ownership could be spread out among many individuals.
Furthermore, bitcoin ownership can also be anonymous, as users can create multiple addresses to store their bitcoin or use privacy-focused tools such as mixers or tumblers. This makes it difficult to accurately track ownership and determine the true distribution of bitcoin.
In conclusion, while the distribution of bitcoin ownership may not be entirely equal, it’s constantly evolving and may become more decentralized as adoption continues to grow. Regardless of ownership concentration, bitcoin remains a unique and revolutionary technology that has the potential to change the way we think about money and financial transactions.
Comparing Bitcoin to Other Cryptocurrencies
If you’re new to the world of cryptocurrency, you might be wondering what sets Bitcoin apart from other digital currencies. While Bitcoin was the first decentralized digital currency, there are now thousands of different cryptocurrencies available for trading and investment. So let’s take a closer look at how Bitcoin compares to other cryptocurrencies.
One of the biggest differences between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is their market cap. Bitcoin is by far the largest cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalization, accounting for over 50% of the entire crypto market. Other popular cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Binance Coin, and Cardano have market caps that are a fraction of Bitcoin’s size.
Another key difference is the technology behind each cryptocurrency. Bitcoin uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This requires significant amounts of computational power and energy consumption. In contrast, newer cryptocurrencies like Cardano and Solana use more energy-efficient consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or Proof-of-History (PoH).
Transaction fees also vary widely between different cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin has notoriously high transaction fees during times of high network congestion, which can make small transactions expensive to process. Other cryptocurrencies like Litecoin and Bitcoin Cash were created specifically to address this issue, with faster transaction times and lower fees.
Finally, the adoption and acceptance of each cryptocurrency also plays a role in its value and popularity. Bitcoin is widely accepted as a form of payment by businesses and individuals around the world, and it has become a mainstream investment option for many. Other cryptocurrencies are still working to gain broader acceptance and recognition.
In conclusion, while Bitcoin remains the dominant cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalization and adoption, there are many other digital currencies with unique features and advantages. Understanding the differences between these cryptocurrencies can help investors and traders make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources.
The Economics of Bitcoin Production
Bitcoin has been a hot topic in the world of finance for several years now. It is a decentralized digital currency that operates without a central bank or administrator, which makes it stand out from traditional currencies. But have you ever wondered how bitcoins are produced? In this article, we will dive into the economics of bitcoin production.
Bitcoin mining is the process of creating new bitcoins by solving complex mathematical equations. Miners use powerful computers to solve these equations and verify transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. As a reward for their efforts, miners receive newly created bitcoins.
The production of bitcoins is limited to 21 million coins, and as of this writing, around 18.7 million bitcoins have already been mined. This means that there are only a few bitcoins left to be mined, making the process more difficult and expensive than ever before.
The cost of producing bitcoins varies depending on several factors, such as electricity costs, hardware expenses, and mining difficulty. The mining difficulty is adjusted every 2016 blocks to ensure that the average time it takes to mine a block remains at 10 minutes. If the computing power used for mining increases, the mining difficulty also increases, making it more challenging to mine bitcoins.
One crucial factor that affects the economics of bitcoin production is the price of bitcoin itself. When the price of bitcoin is high, it becomes more profitable to mine bitcoins. But when the price drops, mining becomes less profitable, and some miners may even shut down their operations.
In conclusion, the economics of bitcoin production are complex and constantly changing. The cost of producing bitcoins depends on various factors, including electricity costs, hardware expenses, mining difficulty, and the price of bitcoin itself. As bitcoins become scarcer, the mining process becomes more challenging and expensive, making it harder for miners to profit from their efforts.
The Impact of Bitcoin’s Fixed Supply
Bitcoin, the world’s largest cryptocurrency, has a fixed supply of 21 million coins. This means that there will never be more than 21 million bitcoins in existence, regardless of increasing demand or adoption. While this may seem like a limitation, it is actually one of the core strengths of Bitcoin that sets it apart from traditional currencies.
One of the main impacts of Bitcoin’s fixed supply is its deflationary nature. Unlike fiat currencies that can be printed at will by central banks, the limited supply of Bitcoin means that its value is not subject to inflationary pressures. As demand for Bitcoin increases, its price is likely to rise due to its scarcity, making it an attractive investment asset for many individuals and institutions.
Furthermore, Bitcoin’s fixed supply also helps to safeguard against inflation caused by economic crises. In times of economic instability, governments may resort to printing more money to stimulate the economy. However, this often leads to inflation and devalues the currency. With Bitcoin’s fixed supply, there is no risk of government intervention or manipulation, making it a safe haven for investors looking to protect their wealth.
Another impact of Bitcoin’s fixed supply is its potential to revolutionize the global financial system. As a decentralized currency, Bitcoin operates outside of traditional banking systems, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions across borders. With a fixed supply, Bitcoin is not subject to the whims of governments or financial institutions, making it a powerful tool for individuals and businesses seeking greater financial autonomy and security.
In conclusion, the impact of Bitcoin’s fixed supply cannot be overstated. It provides a hedge against inflation, offers a safe haven for investors, and has the potential to transform the way we think about and interact with money. As adoption and demand for Bitcoin continue to grow, its fixed supply will become an increasingly valuable asset in the global financial landscape.
The Relationship Between Bitcoin’s Supply and Demand
Bitcoin is a digital currency that has taken the world by storm since its inception in 2009. Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning that it’s not controlled by any central authority. Instead, transactions are verified by a network of users, making it completely secure and transparent.
One of the most interesting aspects of Bitcoin is its supply and demand dynamics. In the beginning, Bitcoin had a fixed supply of 21 million coins, which were slowly released into circulation through a process called mining. As more people became interested in Bitcoin, the demand for it increased, causing its value to soar.
The relationship between Bitcoin’s supply and demand can be compared to that of gold. Like gold, Bitcoin’s limited supply makes it a scarce resource, which is highly sought after. However, unlike gold, Bitcoin can be easily transferred and traded online, making it a much more convenient investment option.
As demand for Bitcoin continues to grow, so too does its value. This can be seen in the recent price surges, where Bitcoin reached an all-time high of nearly $65,000 per coin. However, as with any investment, there are risks involved, and Bitcoin’s value can be affected by various factors such as government regulations, market trends, and investor sentiment.
Another interesting aspect of Bitcoin’s supply and demand dynamics is the effect that halving events have on its value. Every four years, the number of Bitcoins rewarded to miners for verifying transactions is cut in half. This means that the rate at which new Bitcoins are introduced into circulation slows down, effectively reducing the supply of Bitcoin. As a result, many analysts believe that these halving events contribute to the cyclical nature of Bitcoin’s price movements.
In conclusion, Bitcoin’s supply and demand dynamics play a crucial role in determining its value. With a limited supply and growing demand, Bitcoin has become a highly sought-after investment option. While its value may be subject to fluctuations, many investors believe that Bitcoin’s long-term potential is worth the risk.